4.5 KiB
YOSO
Overview
The YOSO model was proposed in You Only Sample (Almost) Once: Linear Cost Self-Attention Via Bernoulli Sampling
by Zhanpeng Zeng, Yunyang Xiong, Sathya N. Ravi, Shailesh Acharya, Glenn Fung, Vikas Singh. YOSO approximates standard softmax self-attention
via a Bernoulli sampling scheme based on Locality Sensitive Hashing (LSH). In principle, all the Bernoulli random variables can be sampled with
a single hash.
The abstract from the paper is the following:
Transformer-based models are widely used in natural language processing (NLP). Central to the transformer model is the self-attention mechanism, which captures the interactions of token pairs in the input sequences and depends quadratically on the sequence length. Training such models on longer sequences is expensive. In this paper, we show that a Bernoulli sampling attention mechanism based on Locality Sensitive Hashing (LSH), decreases the quadratic complexity of such models to linear. We bypass the quadratic cost by considering self-attention as a sum of individual tokens associated with Bernoulli random variables that can, in principle, be sampled at once by a single hash (although in practice, this number may be a small constant). This leads to an efficient sampling scheme to estimate self-attention which relies on specific modifications of LSH (to enable deployment on GPU architectures). We evaluate our algorithm on the GLUE benchmark with standard 512 sequence length where we see favorable performance relative to a standard pretrained Transformer. On the Long Range Arena (LRA) benchmark, for evaluating performance on long sequences, our method achieves results consistent with softmax self-attention but with sizable speed-ups and memory savings and often outperforms other efficient self-attention methods. Our code is available at this https URL
This model was contributed by novice03. The original code can be found here.
Usage tips
- The YOSO attention algorithm is implemented through custom CUDA kernels, functions written in CUDA C++ that can be executed multiple times in parallel on a GPU.
- The kernels provide a
fast_hashfunction, which approximates the random projections of the queries and keys using the Fast Hadamard Transform. Using these hash codes, thelsh_cumulationfunction approximates self-attention via LSH-based Bernoulli sampling. - To use the custom kernels, the user should set
config.use_expectation = False. To ensure that the kernels are compiled successfully, the user must install the correct version of PyTorch and cudatoolkit. By default,config.use_expectation = True, which uses YOSO-E and does not require compiling CUDA kernels.
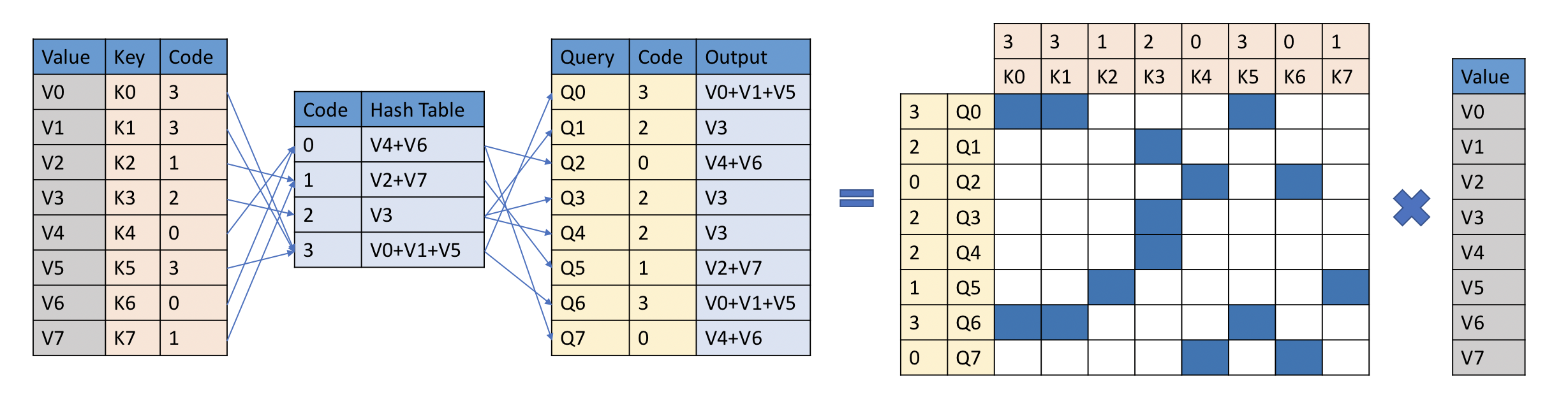
YOSO Attention Algorithm. Taken from the original paper.
Resources
- Text classification task guide
- Token classification task guide
- Question answering task guide
- Masked language modeling task guide
- Multiple choice task guide
YosoConfig
autodoc YosoConfig
YosoModel
autodoc YosoModel - forward
YosoForMaskedLM
autodoc YosoForMaskedLM - forward
YosoForSequenceClassification
autodoc YosoForSequenceClassification - forward
YosoForMultipleChoice
autodoc YosoForMultipleChoice - forward
YosoForTokenClassification
autodoc YosoForTokenClassification - forward
YosoForQuestionAnswering
autodoc YosoForQuestionAnswering - forward