6.5 KiB
Audio Spectrogram Transformer
Overview
The Audio Spectrogram Transformer model was proposed in AST: Audio Spectrogram Transformer by Yuan Gong, Yu-An Chung, James Glass. The Audio Spectrogram Transformer applies a Vision Transformer to audio, by turning audio into an image (spectrogram). The model obtains state-of-the-art results for audio classification.
The abstract from the paper is the following:
In the past decade, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have been widely adopted as the main building block for end-to-end audio classification models, which aim to learn a direct mapping from audio spectrograms to corresponding labels. To better capture long-range global context, a recent trend is to add a self-attention mechanism on top of the CNN, forming a CNN-attention hybrid model. However, it is unclear whether the reliance on a CNN is necessary, and if neural networks purely based on attention are sufficient to obtain good performance in audio classification. In this paper, we answer the question by introducing the Audio Spectrogram Transformer (AST), the first convolution-free, purely attention-based model for audio classification. We evaluate AST on various audio classification benchmarks, where it achieves new state-of-the-art results of 0.485 mAP on AudioSet, 95.6% accuracy on ESC-50, and 98.1% accuracy on Speech Commands V2.
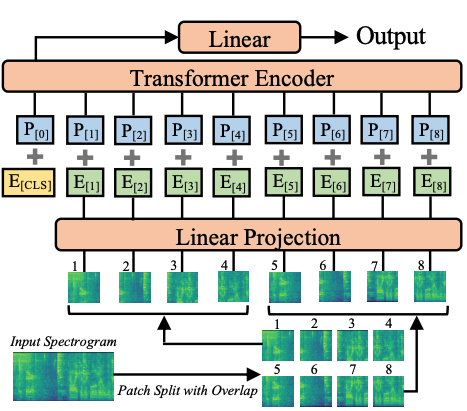
Audio Spectrogram Transformer architecture. Taken from the original paper.
This model was contributed by nielsr. The original code can be found here.
Usage tips
- When fine-tuning the Audio Spectrogram Transformer (AST) on your own dataset, it's recommended to take care of the input normalization (to make
sure the input has mean of 0 and std of 0.5). [
ASTFeatureExtractor] takes care of this. Note that it uses the AudioSet mean and std by default. You can checkast/src/get_norm_stats.pyto see how the authors compute the stats for a downstream dataset. - Note that the AST needs a low learning rate (the authors use a 10 times smaller learning rate compared to their CNN model proposed in the PSLA paper) and converges quickly, so please search for a suitable learning rate and learning rate scheduler for your task.
Using Scaled Dot Product Attention (SDPA)
PyTorch includes a native scaled dot-product attention (SDPA) operator as part of torch.nn.functional. This function
encompasses several implementations that can be applied depending on the inputs and the hardware in use. See the
official documentation
or the GPU Inference
page for more information.
SDPA is used by default for torch>=2.1.1 when an implementation is available, but you may also set
attn_implementation="sdpa" in from_pretrained() to explicitly request SDPA to be used.
from transformers import ASTForAudioClassification
model = ASTForAudioClassification.from_pretrained("MIT/ast-finetuned-audioset-10-10-0.4593", attn_implementation="sdpa", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
...
For the best speedups, we recommend loading the model in half-precision (e.g. torch.float16 or torch.bfloat16).
On a local benchmark (A100-40GB, PyTorch 2.3.0, OS Ubuntu 22.04) with float32 and MIT/ast-finetuned-audioset-10-10-0.4593 model, we saw the following speedups during inference.
| Batch size | Average inference time (ms), eager mode | Average inference time (ms), sdpa model | Speed up, Sdpa / Eager (x) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 27 | 6 | 4.5 |
| 2 | 12 | 6 | 2 |
| 4 | 21 | 8 | 2.62 |
| 8 | 40 | 14 | 2.86 |
Resources
A list of official Hugging Face and community (indicated by 🌎) resources to help you get started with the Audio Spectrogram Transformer.
- A notebook illustrating inference with AST for audio classification can be found here.
- [
ASTForAudioClassification] is supported by this example script and notebook. - See also: Audio classification.
If you're interested in submitting a resource to be included here, please feel free to open a Pull Request and we'll review it! The resource should ideally demonstrate something new instead of duplicating an existing resource.
ASTConfig
autodoc ASTConfig
ASTFeatureExtractor
autodoc ASTFeatureExtractor - call
ASTModel
autodoc ASTModel - forward
ASTForAudioClassification
autodoc ASTForAudioClassification - forward